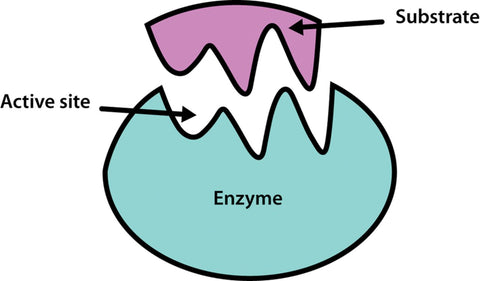
Enzymes are molecules naturally present in the body that help to break apart substances so that they can be used by the body. They usually end in the letters "-ase."
For example, lactase breaks down lactose (milk sugar) and lipase breaks down lipids (fats).
All living things produce their own enzymes. Without these enzymes we would not be able to sustain life.
The lack of enzymes in the diet is the cause of many illnesses including indigestion, constipation, bloating, fatigue and headaches. Fresh and raw food, especially fruit and vegetables are full of enzymes.
Dietary experts suggest that eating vegetables at the start of a meal floods the stomach and intestines with digestive enzymes that help to break down the food that is about to come.
Raw organic honey contains an astonishing number of enzymes, in fact over 5000 different enzymes according to nutrition expert Sally Fallon of the Weston A. Price Foundation.
These enzymes have an immediate detoxifying effect on the body because they get to work straight away and start breaking down the body's toxins.
The detoxifiying effect is multiplied many times when the raw honey is taken mixed in cold or warm water.
Sally Fallon described a Russian study which tried to find out why many inhabitants of Georgia lived to the age of 100.
The study revealed, as Fallon writes, "Many of these centenarians were beekeepers who often ate raw, unprocessed honey with all its 'impurities,' that is, with the pollen."
The enzymes present in raw organic honey come from both the bees themselves and the plant nectar on which they feed.
Some of these enzymes are:
Diastase
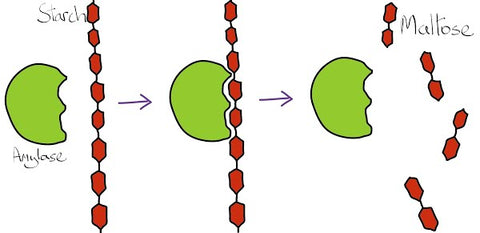
Also known as amylase, digests complex carbohydrates into simple compounds that can be absorbed by the body. Complex carbohydrates include foods such as rice, pasta, grains, potatoes and bread.
The diastase content of honey varies according to the floral source. For example, clover honey has a Diastase Number (DN) of 5.73 whereas eucalyptus (gum) honey has a a Diastase Number of 24.0, almost four times as much.
Our Raw Organic Rivera Gum Honey is one of the world's purest eucalyptus honeys, with a eucalyptus pollen count of over 85-90% eucalyptus.
Diastase content decreases when honey is heated or stored for a long time.
Invertase
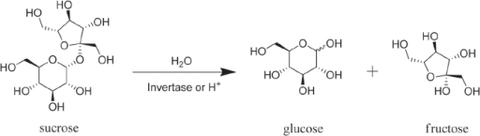
Invertase breaks down sucrose - as found in simple sugar - into glucose and fructose. In other words, invertase helps the body to digest sugar.
Glucose oxidase
Glucose oxidase produces hydrogen peroxide, which is where the powerful antibacterial properties of raw honey come from.
Peptidase
Peptidase is known as a proteolytic enzyme whose function is to break down proteins into amino acids, i.e. to allow proteins to be better absorbed by the body.
The best way to benefit from the high enzyme content of raw honey is to mix a teaspoon of raw honey into a glass of cold or warm (not hot) water and drink it on an empty stomach first thing in the morning.
Flooding the body with digestive enzymes at the start of the day improves digestion because it puts less of a burden on the body to produce these enzymes itself.
Our honeys with particularly high enzyme contents include the 20+ Active Raw Organic Coffee Bean Honey and 10+ Active Raw Organic Orange Blossom Honey. From our standard range, the Raw Organic Pink Lychee Honey from Mexico and the Raw Organic Rainforest Honey from Brazil are particularly high in enzymes.





